Accessible Target Sizes Cheatsheet
Rage taps are annoying and frustrating. These wonderful occurrences in our interface when we need to tap twice or sometimes three times to continue our journeys. Of course, sometimes they happen because the website is too slow, but sometimes it’s the target size of interactive elements that is the culprit.

So how big should our interactive elements be these days? What would be a reliable size for icons, links and buttons — in navigation and on mobile? How do we make it more difficult for our users to make mistakes? Let’s take a look.
Note: You can find a whole video chapter on designing for touch in Smart Interface Design Patterns as well — along with 30 other chapters all around UX and design patterns.
Target Sizes Cheatsheet
One of the common recommendations for target sizes on mobile is 44×44px. This is a little bit misleading because screen pixels, or at least device-independent pixels (dips) are scaled to a multiple of the display resolution. So pixels are different on different screens, and when we have a conversation about sizes, we probably should be speaking about dips, rather than pixels.

Depending on where an element appears on the screen, it needs more or less padding. In general, we are very precise in our input in the center of the screen, but we are least precise on the edges of the screen (both on the top and at the bottom).
Accordion to Steven Hoober’s research in his book on Touch Design For Mobile Interfaces, to minimize rage taps, we need to aim for 11mm (or 31pt / 42px) on the top of the screen, and 12mm (or 34pt / 46px) at the bottom of the screen. In the center though, we could potentially go as low as 7mm (or 20pt / 27px). This includes both the width and padding of an interactive element.
How do point units translate to CSS pixels or Android/iOS units? Fortunately, Steven Hoober provides a helpful conversion table to help you translate from points to px and em units, Android SPs or DPs, iOS points and Windows DIP or px.
Not All Pixels Are The Same
As we’ve seen above, target sizes change depending on where components appear on the screen. It’s worth noting that according to the WCAG 2.1 AAA level requirements, all targets should measure at least 44 by 44px, except if the target is in a sentence or block of text. For such exceptions, we could be using 27px as a goal, but in general, the larger, the better.

For sticky menus at the top or bottom of the screen, we should probably aim for around 44–46px boxes, or preferably even more. However, for links that appear on the screen as the user scrolls down the page, we probably will be able to avoid most issues with smaller components.

This is also why we probably will be able to place at most five items in the bottom tabs on a mobile phone. Instead, we might need to use a bottom sheet that would slide up from down as an overlay on top of the screen.
Prefer “Actions” Button To Single Icons For Data Tables
Complex tables typically have hover actions that appear once a user starts hovering over a particular row. They typically include everything from highlight and export to move and delete.
In testing, showing icons on hover produces too many mistakes: not only do users often accidentally jump to a wrong row as they navigate horizontally towards the icons. They also make mistakes by accidentally clicking on the wrong spot and starting all over again.

To avoid rage clicks, it might be a good idea to test how well an “Actions” buttons or a “Split”-Button would perform instead. Indeed, that button could live on every row, would open on tap/click, and wouldn’t close automatically. It might not be ideal for every use case, but it definitely gives users more sense of control as they need to take action in a row.

Provide An Assistant For Complex Manipulations
With complex manipulation, such as rotation of an image, or selection of a small part of a larger area, we often rely on pinch and zoom or zoom in/out buttons. These options, of course, work, but they easily become a bit tedious to use for very precise manipulations — especially if used for a while.

Instead, we can attach a little handle to allow users to move their selection within the object faster and with more precision. This is how Tylko allows users to customize their shelves on mobile. Zooming is supported as well, but it’s not necessary to select one of the areas.
When Multiple Taps Are Better Than One
But what do we do if some tap areas have to be small? Perhaps we can’t reserve 27×27px for each icon — for example, when we suggest a color selection in an eCommerce site? Well, in that case, one option to consider would be to prompt a “proper” selection of colors with one additional tap. This might be a bit slower in interaction, but way more accurate.
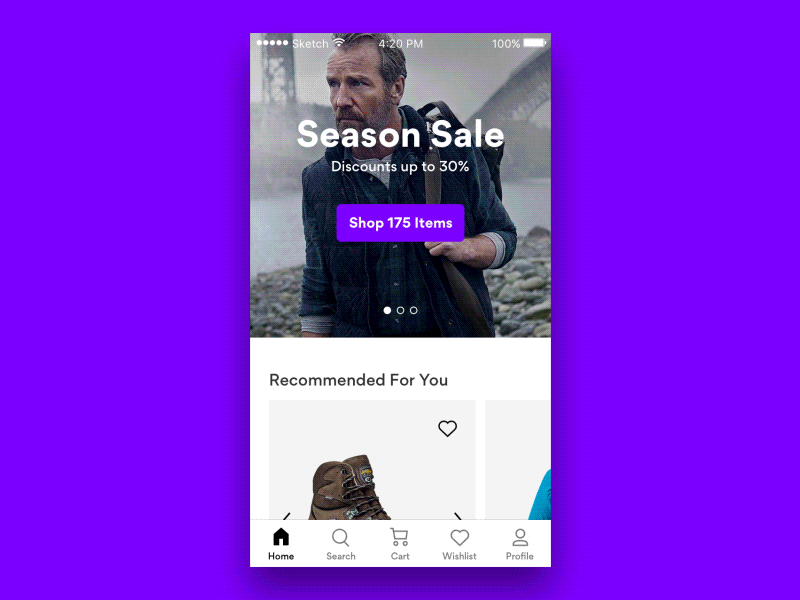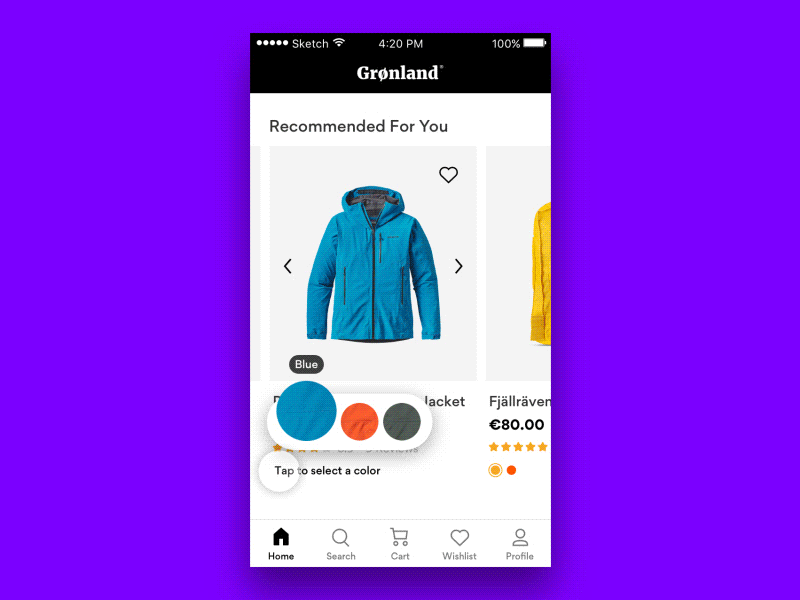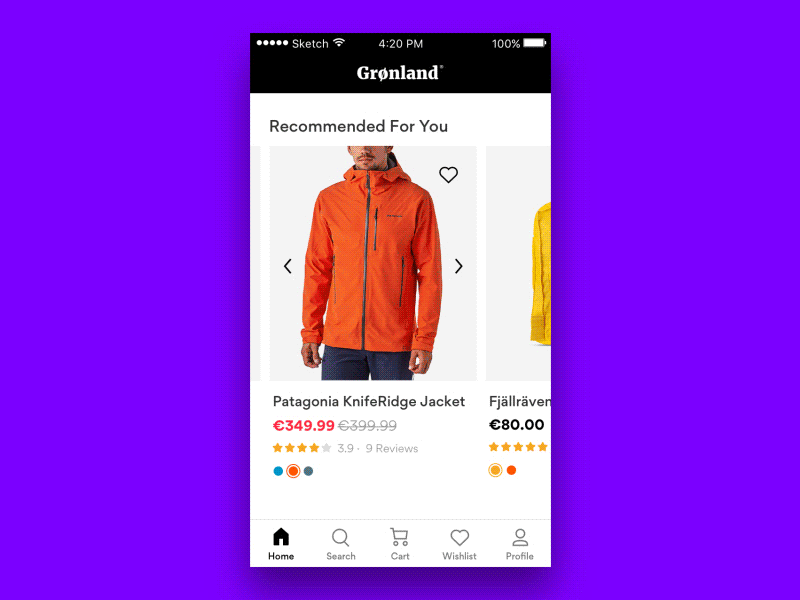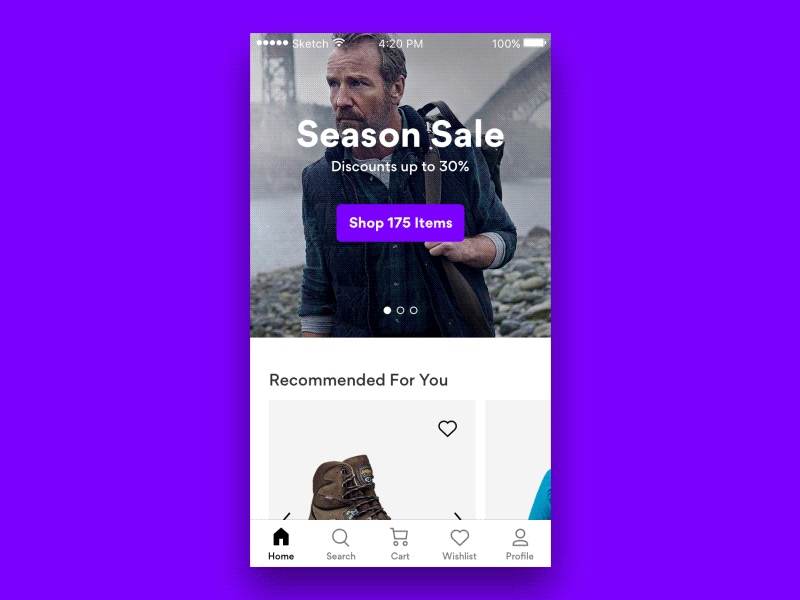
Always Maximize Clickable Area
Whenever possible, encapsulate the entire element, along with enough padding to ensure that you hit the magical 42–46px size to prevent rage taps for good. This typically means adding enough padding for icons but also preferring full-width or full-height bars for accordions and navigation.


Ahmad Shadeed presents a few useful examples of using spacing to increase clickable areas and prevent rage clicks. Any Lupe provides even more suggestions in her article on accessible target sizes.
Wrapping Up
When designing for touch today, we need to use at least 27×27px for small links or icons in the content area and at least 44×44px for icons at the top and at the bottom of the page.

Personally, I would always go up to 30×30px and 48×48px to make sure mistakes are really difficult to make. And, of course, always use full width or full height for the clickable areas. Hopefully, this will help us remove any possible rage taps from our websites altogether — and many of your users will sincerely appreciate it indeed.
You can find more details on navigation UX in the video library on Smart Interface Design Patterns 🍣 — with a live UX training that’s coming up in September this year.
Useful Resources
There are a few wonderful resources on accessible target sizes that might be helpful if you’d like to dive deeper in the topic:
- “Accessible Target Sizes,” by Amy Lupe
- “Touch Targets on Touchscreens,” by Aurora Hailey
- “Enhancing the Clickable Area,” by Ahmad Shadeed
- “WCAG 2.55 for Better Target Sizes,” by Todd Libby
- “Fitt’s Law In The Touch Era,” by Steven Hoober
- “Touch Design For Mobile Interfaces,” by Steven Hoober
- “Type Sizes for Every Device,” by Steven Hoober




 Register for free to attend Axe-con
Register for free to attend Axe-con Register Free Now
Register Free Now
 Celebrating 10 million developers
Celebrating 10 million developers SurveyJS: White-Label Survey Solution for Your JS App
SurveyJS: White-Label Survey Solution for Your JS App

